Highlights
-
Searches for heavy neutrinos at a 3 TeV CLIC in fat jet final states
2026, 50(3): 033110. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ae2d24
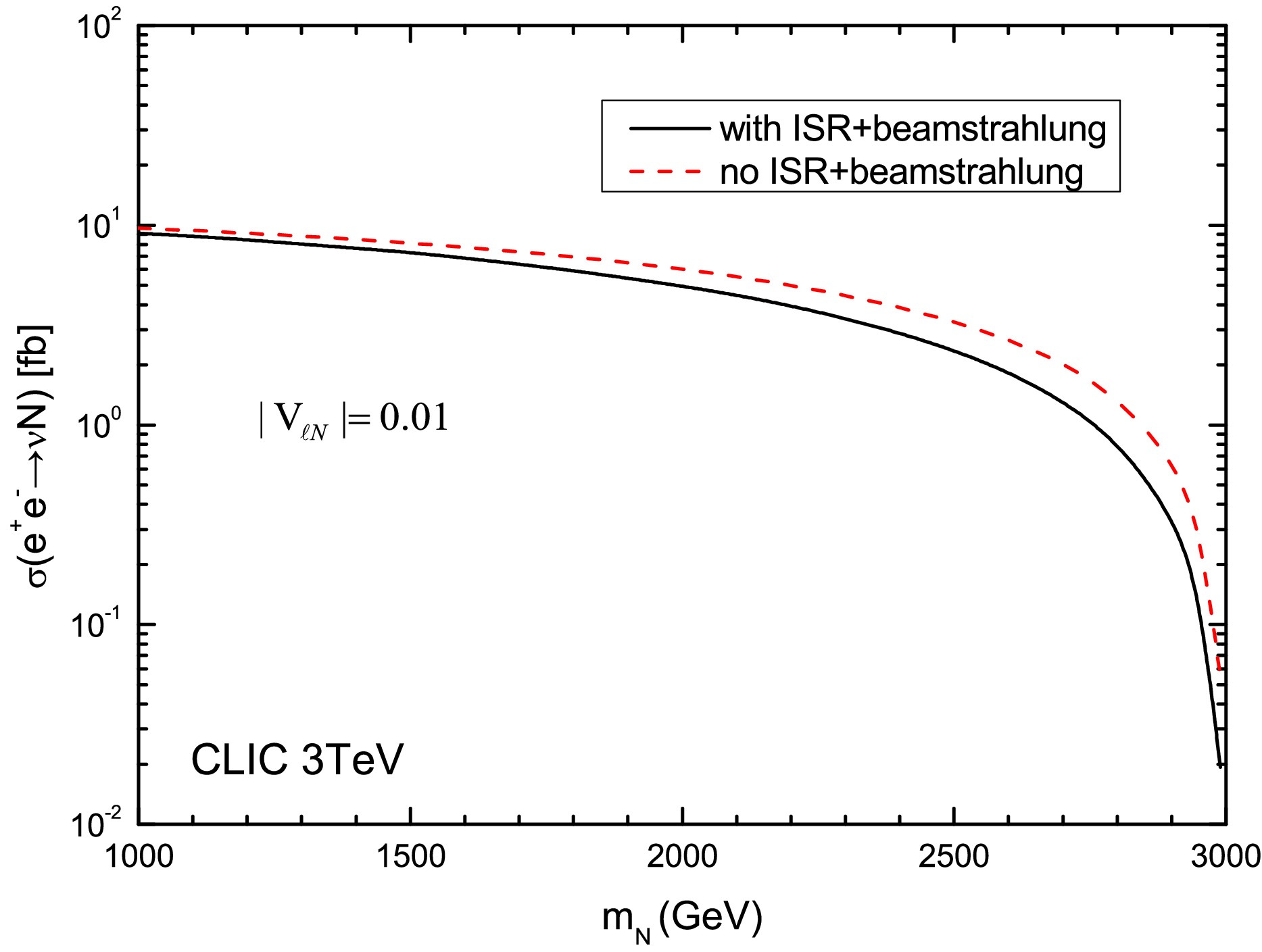 Heavy Majorana neutrinos (N) are predicted in many models of physics beyond the Standard Model. In this work, we explore the production and detection prospects of TeV-scale heavy neutrinos ($ m_N \gtrsim 1 $ TeV) at a future 3 TeV Compact Linear Collider (CLIC). We focus on two distinct decay topologies: (i) $ N \to \ell^\pm W^\mp $ with hadronic W boson decay, leading to a final state with one charged lepton and a hadronic fat jet $ J_W $; and (ii) $ N \to \nu h $ with subsequent Higgs decay $ h \to b\bar{b} $, yielding a Higgs-tagged fat jet $ J_h $ and $\not{E}_T$. Based on comprehensive detector-level simulations and background analysis, we present both $ 2\sigma $ exclusion limits and $ 5\sigma $ discovery reaches in the $ m_N $–$ |V_{\ell N}|^2 $ plane. We further extract 95% confidence level upper limits on the mixing parameter $ |V_{\ell N}|^2 $ and perform a detailed comparison with existing constraints from direct searches at future colliders and indirect global fits. Our findings demonstrate that a 3 TeV CLIC can improve the sensitivity to $ |V_{\ell N}|^2 $ by about two orders of magnitude compared with the projected reaches of future hadron colliders while remaining competitive with other CLIC search channels.
Heavy Majorana neutrinos (N) are predicted in many models of physics beyond the Standard Model. In this work, we explore the production and detection prospects of TeV-scale heavy neutrinos ($ m_N \gtrsim 1 $ TeV) at a future 3 TeV Compact Linear Collider (CLIC). We focus on two distinct decay topologies: (i) $ N \to \ell^\pm W^\mp $ with hadronic W boson decay, leading to a final state with one charged lepton and a hadronic fat jet $ J_W $; and (ii) $ N \to \nu h $ with subsequent Higgs decay $ h \to b\bar{b} $, yielding a Higgs-tagged fat jet $ J_h $ and $\not{E}_T$. Based on comprehensive detector-level simulations and background analysis, we present both $ 2\sigma $ exclusion limits and $ 5\sigma $ discovery reaches in the $ m_N $–$ |V_{\ell N}|^2 $ plane. We further extract 95% confidence level upper limits on the mixing parameter $ |V_{\ell N}|^2 $ and perform a detailed comparison with existing constraints from direct searches at future colliders and indirect global fits. Our findings demonstrate that a 3 TeV CLIC can improve the sensitivity to $ |V_{\ell N}|^2 $ by about two orders of magnitude compared with the projected reaches of future hadron colliders while remaining competitive with other CLIC search channels. -
Particle-number conserving analysis of the πd5/2 band in 117,119,121,123,125Cs
2026, 50(3): 034107. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ae1de6
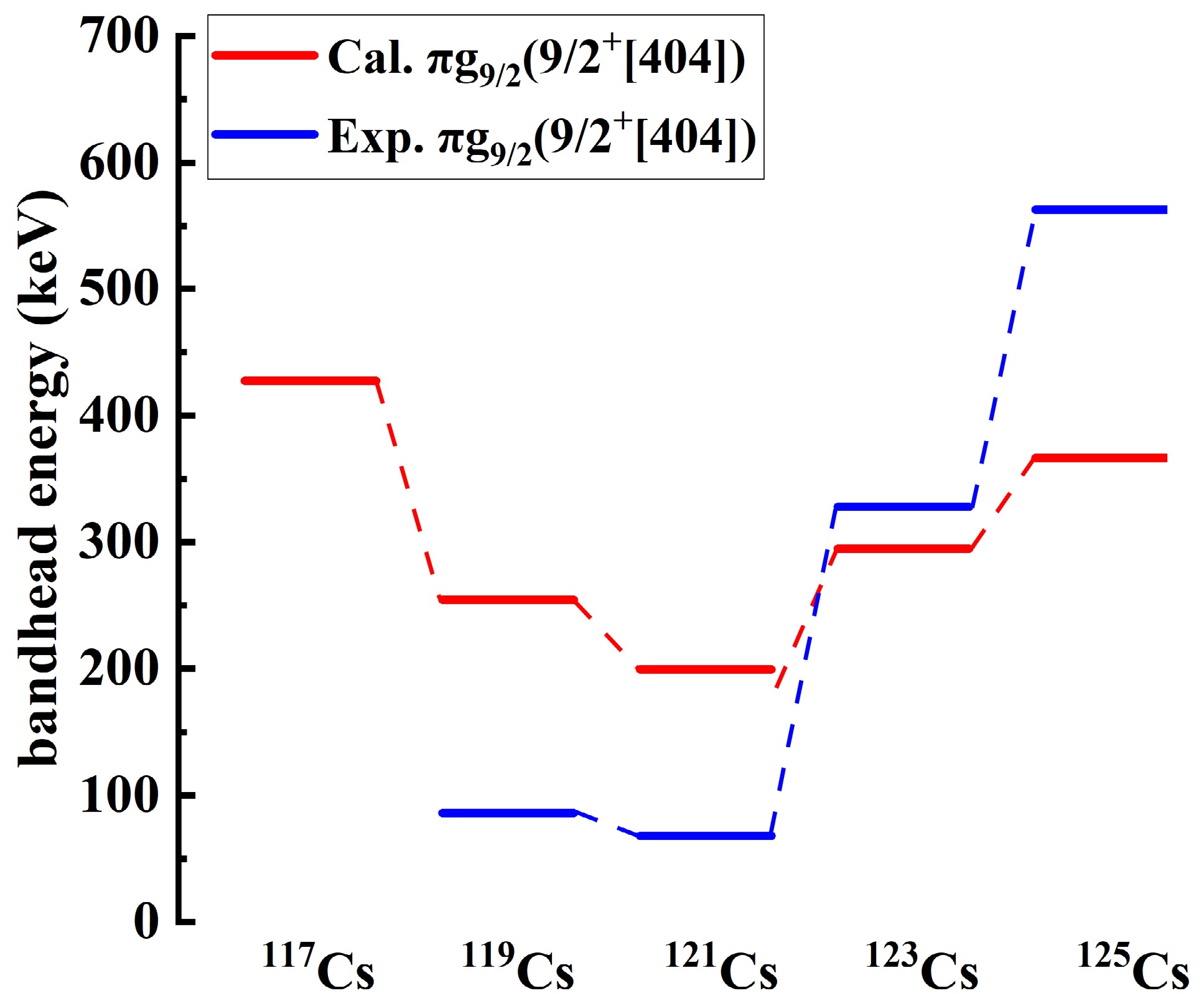 The $ \pi d_{5/2} $ rotational bands in odd-even nuclei 117,119,121,123,125Cs are systematically investigated using the cranked shell model (CSM) with the pairing correlations modeled with a particle number conserving (PNC) method. In this PNC method, the particle number is conserved exactly while considering the blocking effects. The experimental observations of the $ \pi d_{5/2} $ bands with two upbendings for 117,119Cs and one backbending for 125Cs are reproduced very well by the PNC-CSM method. Furthermore, $ \pi d_{5/2} $ configuration bands with two upbendings for 121Cs and one backbending for 123Cs are predicted by the PNC-CSM calculations. The difference between the lighter 117,119,121Cs and heavier 123,125Cs isotopes is caused by the evolution of single-particle orbitals near the Fermi surface, and the high-j low-Ω orbital $ \pi [550]1/2 $ plays an important role. The proton shell gap of lighter isotopes is at $ Z=50 $, whereas it appears at $ Z=48 $ for heavier ones. For lighter isotopes 117,119,121Cs, the first upbending is primarily due to the off-diagonal contributions of protons $ j_{x}(\pi5/2^{-}[532]\pi3/2^{-}[541]) $ and $ j_{x}(\pi1/2^{-}[550]\pi3/2^{-}[541]) $. The second upbending is mainly effected by the off-diagonal contributions of neutrons $ j_{x}(\nu7/2^{-}[523] \nu5/2^{-}[532]) $ and $ j_{x}(\nu3/2^{-}[541] \nu5/2^{-}[532]) $ for 117,119Cs and $ j_{x}(\nu1/2^{-}[541] \nu5/2^{-}[532]) $ for 121Cs, respectively. For heavier isotopes such as 123,125Cs, the backbending is attributed mainly to the diagonal parts of proton $ j_{x}(\pi1/2^{-}[550]) $ and neutron $ \nu7/2^{-}[523] $ orbital related terms of diagonal $ j_{x}(\nu7/2^{-}[523]) $ and off-diagonal $ j_{x}(\nu7/2^{-}[523] \nu5/2^{-}[532]) $ contributions.
The $ \pi d_{5/2} $ rotational bands in odd-even nuclei 117,119,121,123,125Cs are systematically investigated using the cranked shell model (CSM) with the pairing correlations modeled with a particle number conserving (PNC) method. In this PNC method, the particle number is conserved exactly while considering the blocking effects. The experimental observations of the $ \pi d_{5/2} $ bands with two upbendings for 117,119Cs and one backbending for 125Cs are reproduced very well by the PNC-CSM method. Furthermore, $ \pi d_{5/2} $ configuration bands with two upbendings for 121Cs and one backbending for 123Cs are predicted by the PNC-CSM calculations. The difference between the lighter 117,119,121Cs and heavier 123,125Cs isotopes is caused by the evolution of single-particle orbitals near the Fermi surface, and the high-j low-Ω orbital $ \pi [550]1/2 $ plays an important role. The proton shell gap of lighter isotopes is at $ Z=50 $, whereas it appears at $ Z=48 $ for heavier ones. For lighter isotopes 117,119,121Cs, the first upbending is primarily due to the off-diagonal contributions of protons $ j_{x}(\pi5/2^{-}[532]\pi3/2^{-}[541]) $ and $ j_{x}(\pi1/2^{-}[550]\pi3/2^{-}[541]) $. The second upbending is mainly effected by the off-diagonal contributions of neutrons $ j_{x}(\nu7/2^{-}[523] \nu5/2^{-}[532]) $ and $ j_{x}(\nu3/2^{-}[541] \nu5/2^{-}[532]) $ for 117,119Cs and $ j_{x}(\nu1/2^{-}[541] \nu5/2^{-}[532]) $ for 121Cs, respectively. For heavier isotopes such as 123,125Cs, the backbending is attributed mainly to the diagonal parts of proton $ j_{x}(\pi1/2^{-}[550]) $ and neutron $ \nu7/2^{-}[523] $ orbital related terms of diagonal $ j_{x}(\nu7/2^{-}[523]) $ and off-diagonal $ j_{x}(\nu7/2^{-}[523] \nu5/2^{-}[532]) $ contributions. -
Comprehensive investigation on baryon number violating nucleon decays involving an axion-like particle
2026, 50(3): 033103. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ae25c9
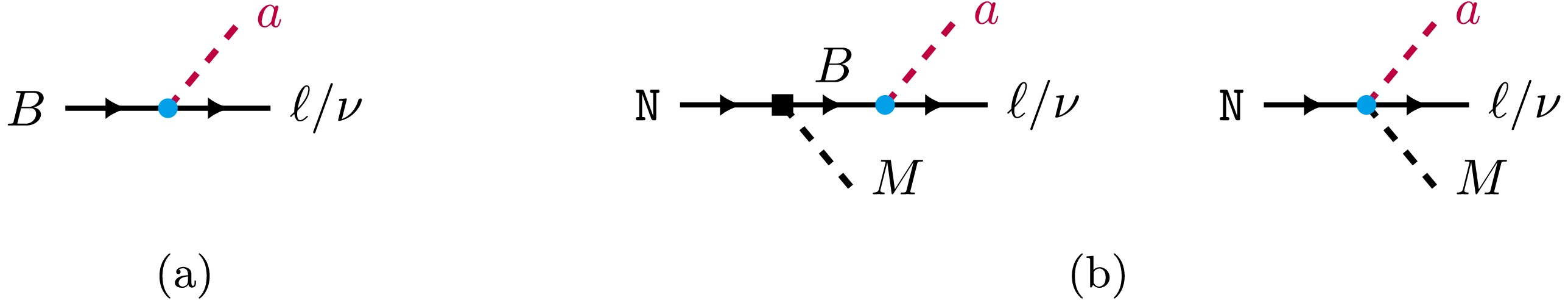 In this study, we systematically investigate baryon number violating (BNV) nucleon decays into an axion-like particle (ALP) within a low energy effective field theory extended with an ALP, which is referred to as aLEFT. Unlike previous studies in the literature, we consider contributions to nucleon decays from a complete set of dimension-eight BNV aLEFT operators involving light u, d, and s quarks. We perform the chiral irreducible representation (irrep) decomposition of these interactions under the QCD chiral group ${S U}(3)_{\mathtt{L}}\times {S U}(3)_{\mathtt{R}}$ and match them onto the recently developed chiral framework to obtain nucleon-level effective interactions among the ALP, octet baryons, and octet pseudoscalar mesons. Within this framework, we derive general expressions for the decay widths of nucleon two- and three-body decays involving an ALP. Subsequently, we analyze momentum distributions for three-body modes and find that operators belonging to the newly identified chiral irreps ${\bf{6}}_{{\mathtt{L}}({\mathtt{R}})}\times {\bf{3}}_{{\mathtt{R}}({\mathtt{L}})}$ exhibit markedly different behavior compared to that in the usual irreps ${\bf{8}}_{{\mathtt{L}}({\mathtt{R}})}\times \pmb{1}_{{\mathtt{R}}({\mathtt{L}})}$ and ${\bf{3}}_{{\mathtt{L}}({\mathtt{R}})}\times \bar{{\bf{3}}}_{{\mathtt{R}}({\mathtt{L}})}$. In addition, we reanalyze experimental data collected by Super-Kamiokande and establish bounds on the inverse decay widths of these new modes by properly accounting for experimental efficiencies and Cherenkov threshold effects because of the lack of direct constraints on those exotic decay modes. Our recasting constraints are several orders of magnitude more stringent than inclusive bounds used in the literature. Based on these improved bounds, we set conservative limits on associated effective scales across a broad range of ALP mass and predict stringent bounds on certain neutron and hyperon decays involving an ALP.
In this study, we systematically investigate baryon number violating (BNV) nucleon decays into an axion-like particle (ALP) within a low energy effective field theory extended with an ALP, which is referred to as aLEFT. Unlike previous studies in the literature, we consider contributions to nucleon decays from a complete set of dimension-eight BNV aLEFT operators involving light u, d, and s quarks. We perform the chiral irreducible representation (irrep) decomposition of these interactions under the QCD chiral group ${S U}(3)_{\mathtt{L}}\times {S U}(3)_{\mathtt{R}}$ and match them onto the recently developed chiral framework to obtain nucleon-level effective interactions among the ALP, octet baryons, and octet pseudoscalar mesons. Within this framework, we derive general expressions for the decay widths of nucleon two- and three-body decays involving an ALP. Subsequently, we analyze momentum distributions for three-body modes and find that operators belonging to the newly identified chiral irreps ${\bf{6}}_{{\mathtt{L}}({\mathtt{R}})}\times {\bf{3}}_{{\mathtt{R}}({\mathtt{L}})}$ exhibit markedly different behavior compared to that in the usual irreps ${\bf{8}}_{{\mathtt{L}}({\mathtt{R}})}\times \pmb{1}_{{\mathtt{R}}({\mathtt{L}})}$ and ${\bf{3}}_{{\mathtt{L}}({\mathtt{R}})}\times \bar{{\bf{3}}}_{{\mathtt{R}}({\mathtt{L}})}$. In addition, we reanalyze experimental data collected by Super-Kamiokande and establish bounds on the inverse decay widths of these new modes by properly accounting for experimental efficiencies and Cherenkov threshold effects because of the lack of direct constraints on those exotic decay modes. Our recasting constraints are several orders of magnitude more stringent than inclusive bounds used in the literature. Based on these improved bounds, we set conservative limits on associated effective scales across a broad range of ALP mass and predict stringent bounds on certain neutron and hyperon decays involving an ALP.
Just Accepted
More >
-
Probing small-scale anisotropic inflation with stochastic gravitational wave background
Published: 2026-03-01
-
Predictions of nuclear charge radii with the radial basis function approach and linear relationship
Published: 2026-02-26
-
Gluon Wigner distributions with transverse polarization at non-zero skewness
Published: 2026-02-26
Recent
More >
-
Measurement and systematic analysis of the cross sections of the 82Kr(n, p)82Br reaction induced by d-T neutrons
2026, 50(4): 044001-044001-9. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ae3601Show AbstractThe cross section of the 82Kr(n, p)82Br reaction induced by d-T neutrons was measured using the activation method. Incident neutrons are generated through the 3H(d, n)4He reaction. High-purity natural krypton gas held at high pressure was used as the target sample. The neutron energy and its uncertainty were determined based on the Q-value equation of the 3H(d, n)4He reaction and the experimental conditions. The neutron fluence incident on the sample is monitored by the 27Al(n, α)24Na reaction. The eight characteristic gamma rays of the 82Br daughter nucleus were selected to determine its activity by off-line gamma spectrometry using an HPGe detector. The 82Kr(n, p)82Br reaction cross sections with lower uncertainties were finally determined at five neutron energies by the weighted method. The measured cross sections were compared with previous experimental studies, theoretical values from Talys-2.0, calculation results from the systematics (empirical and semi-empirical) formulas, and evaluation results. The present high-precision cross sections for the 82Kr(n, p)82Br reaction over a wide energy range not only help to validate and evaluate nuclear reaction models, but also substantially enrich the neutron-induced nuclear reaction cross sections database.
-
Improving nuclear mass predictions by correcting mass residuals using eXtreme Gradient Boosting
2026, 50(4): 044101-044101-8. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ae25cdShow AbstractNuclear masses are investigated for the first time using the eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) method. Nucleon numbers, valence nucleon numbers, and physical quantities related to the magic number are used as input features for the decision tree, which learns the residuals of experimental binding energies with respect to the Bethe-Weizsäcker (BW2) formula predictions, and the XGBoost method can achieve high accuracy predictions of nuclear binding energy. For nuclear masses of magic number nuclei with prediction challenges, XGBoost can better capture the physical information associated with the magic number compared to that using BW2, and the root mean square deviation of its predicted nuclear mass ranges from 2.769 to 0.732 MeV. Comparing the results of BW2* and XGBoost* with the pseudo-experimental data of Finite-Range Droplet Model (FRDM12) suggests that the XGBoost* method may have better extrapolation abilities.
-
Sub-barrier fusion enhancement caused by positive Q-value four-neutron transfer
2026, 50(4): 044110-044110-10. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ae3731Show AbstractThe effect of positive Q-value four-neutron transfer (PQ4NT) on the sub-barrier capture cross sections is investigated systematically using the empirical barrier distribution (EBD2) method. For 13 fusion reactions with $Q_{4{\rm n}}>0$, the sustained neutron-pair transfer reduces barrier heights and enhances capture cross sections at sub-barrier energies. In contrast, reactions such as 18O+58Ni, which have $Q_{2{\rm n}}>0$ and $Q_{4{\rm n}}<0$, exhibit no enhancement due to stalling of subsequent neutron-pair transfer after the initial 2n transfer. Incorporating PQ4NT effects into EBD2 for systems with $Q_{4{\rm n}}>0$ significantly reduces the average deviation between the predicted and experimental capture cross sections (113 datasets) by 20%. In comparison with those in reactions induced by 48Ca ($Q_{4{\rm n}}<0$), the neutron pickup probabilities in the quasi-elastic scattering of 40Ca-induced reactions ($Q_{4{\rm n}}>0$) are considerably larger, according to the time-dependent Hartree-Fock calculations.
Archive
ISSN 1674-1137 CN 11-5641/O4
Original research articles, Ietters and reviews Covering theory and experiments in the fieids of
- Particle physics
- Nuclear physics
- Particle and nuclear astrophysics
- Cosmology
Author benefits
- A SCOAP3 participating journal - free Open Access publication for qualifying articles
- Average 24 days to first decision
- Fast-track publication for selected articles
- Subscriptions at over 3000 institutions worldwide
- Free English editing on all accepted articles
News
- CPC Announces 2025 Outstanding Reviewers
- Chinese Physics C Outstanding Reviewer Award 2023
- Impact factor of Chinese Physics C is 3.6 in 2022
- 2022 CPC Outstanding Reviewer Awards
- The 2023 Chinese New Year-Office closure
Cover Story
- Cover Story (Issue 2, 2026) |The images of Brans-Dicke-Kerr type naked singularities
- Cover Story (Issue 1, 2026) A focused review of quintom cosmology: from quintom dark energy to quintom bounce
- Cover Story (Issue 11, 2025) The Earth-Magnet Assists DAMPE in Studying Cosmic Anti-Electrons
- Cover Story (Issue 9, 2025): Precise measurement of χc0 resonance parameters and branching fractions of χc0,c2→π+π-/ K+K-
- Cover Story (Issue 8, 2025) A Novel Perspective on Spacetime Perturbations: Bridging Riemannian and Teleparallel Frameworks